What is
an acoustic schwannoma ?
A benign
tumour arising from Schwann cells enclosing the VIIIth cranial nerve. Schwann
cells are not nerve cells themselves, but are responsible for protection and
insulation of nerve cells. The VIIIth nerve is the vestibulocochlear nerve, which
is responsible for hearing and balance.
 |
| Coronal MRI images of acoustic schwannoma at the left CP angle ( arrow) |
Yes. This
tumour arises from the vestibulocohlear nerve. It is also called an acoustic
neurinoma.
What symptoms does a patient suffering from an acoustic schwannoma feel:
· Decreased hearing.
· Tinnitus i.e. hearing a sound in the
ear.
· Loss of balance
· Headache
· In large tumours:
o
facial
paralysis
o
impaired
taste
o
symptoms
arising from pressure on brain stem or other cranial nerves, such as deviation
of tongue, difficulty in swallowing.
 |
| Axial images of acoustic schwannoma of left CP angle |
Can acoustic schwannoma / vestibular schwannoma be treated with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS)?
Stereotactic
radiosurgery is an effective method of treating vestibular schwannomas,
controlling the tumour in more than 90% of patients and hearing in more than 80
% of patients. The tumour does not disappear and in most patients either
decreases slowly or remains the same size.
What is
stereotactic radiosurgery?
Radiosurgery
is the treatment of a lesion in the brain using X or gamma rays in a sharply
focused manner, in a single or limited number of sessions, while ensuring strict
attention to positioning and immobilization of the head.
How do
you treat acoustic schwannomas using radiosurgery?
I treat
patients with acoustic schwannoma using a technique called frameless
radiosurgery. The treatment is delivered on a Novalis Tx linear accelerator, a
very precise radiosurgery delivery platform installed at Indraprastha Apollo
Hospital, New Delhi.
The patient’s
head is immobilized in a thermoplastic cast, that molds into the shape of the
head, and helps to hold it accurately in the same position. A special Brain Lab
cast is used for radiosurgery. This is followed by scanning of the patients
brain, using a CT scan as well as an MR, with
detailed imaging of the brain and neighbouring structures such as the
middle and inner ear. These images are then fused to allow information
regarding the anatomy to be extracted in detail.
The lesion and surrounding
normal structures are delineated by me and my team, following which a team of
medical physicists creates multiple radiosurgery plans, targeting the lesion in
a focused manner. The best plan is then chosen and a quality assurance test
performed to assess whether the chosen plan can accurately be delivered on the
linear accelerator.
 | ||||||
| An acoustic schwannoma (green), and organs at risk, brainstem (purple), cochlea (sea-green), optic nerves and chiasm and eyes (red), in 3D |
Following
this, the patient receives premedication with steroids to counter the effects
of some swelling that may happen following radiosurgery, and is then
transported to the Novalis Tx suite. The treatment is painless and lasts about 40 to 60 minutes. The radiotherapy is delivered
using a sophisticated radiation plan
comprising non co planar fields and arcs.
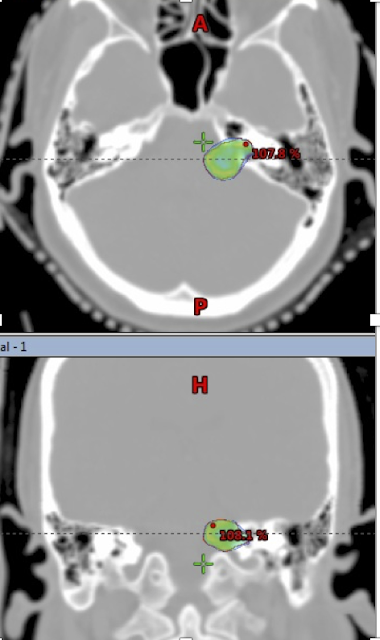 |
| Acoustic Schwannoma (left) outlined in red, in axial and coronal CT images; SRS dose represented by colourwash, closely conforms to the edges of the lesion. |
Attention
to detail, during planning and delivery of radiosurgery, is critical
What special techniques are used to preserve hearing ?
What special techniques are used to preserve hearing ?
Hearing is
preserved using sophisticated radiosurgery planning that restricts the dose to
the cochlea , i.e. the inner ear and a specific component of the cochlea, the
modiolus.
What is
the usual dose schedule used in treating an acoustic schwannoma?
The most
common schedule is a single fraction of radiosurgery, delivering 11-13 Gy to
the edge of the lesion (and a higher dose centrally). Larger lesions may
however be treated using more protracted schedules, comprising 3, 12 or 28
sessions.

No comments:
Post a Comment